Cellulogia is a term that has gradually gained attention in discussions around body aesthetics, skin health, and connective tissue science. While it is often used interchangeably with the more familiar word cellulite, cellulogia represents a broader, more nuanced understanding of the condition. Rather than framing it as a simple cosmetic flaw, cellulogia focuses on the biological, structural, and lifestyle-related factors that influence skin texture and subcutaneous fat behavior.
In recent years, the conversation around cellulogia has shifted dramatically. What was once treated as a beauty problem to be hidden or eliminated is now increasingly discussed as a normal physiological phenomenon. This shift has encouraged more honest, science-based discussions and reduced the stigma associated with uneven skin texture.
This article explores cellulogia from multiple angles—scientific, hormonal, lifestyle-based, and cultural—offering a comprehensive and expert-level overview. The goal is not to promote unrealistic ideals but to provide clarity, understanding, and informed perspectives.
Understanding Cellulogia: What the Term Really Means
Cellulogia refers to the structural changes in subcutaneous fat and connective tissue that result in a dimpled or uneven appearance of the skin. Unlike casual usage of the word cellulite, cellulogia emphasizes the underlying tissue architecture rather than surface appearance alone.
At its core, cellulogia involves the interaction between fat cells, connective tissue fibers, lymphatic flow, and microcirculation. When these systems become imbalanced, fat lobules can push upward against the skin while fibrous connective bands pull downward, creating the characteristic uneven texture.
It is important to note that cellulogia is not a disease. It does not indicate poor health, obesity, or lack of fitness. In fact, people of all body types—including athletes and individuals with low body fat—can experience cellulogia.
By understanding cellulogia as a biological condition rather than a cosmetic failure, we can approach it with greater compassion and realism.
The Biology Behind Cellulogia
The biological foundation of cellulogia lies in the structure of the hypodermis, the layer of tissue beneath the skin. This layer contains fat cells, blood vessels, lymphatic channels, and connective tissue septa that anchor the skin to deeper structures.
In individuals prone to cellulogia, the connective tissue septa tend to be more rigid or vertically oriented. This structural arrangement allows fat cells to bulge upward while the septa tether the skin downward, producing an uneven surface.
Microcirculatory changes also play a role. Reduced blood flow and lymphatic drainage can lead to fluid retention and inflammation, which further exaggerate the appearance of cellulogia. Over time, this can contribute to tissue fibrosis, making the texture more noticeable.
Hormones—especially estrogen—strongly influence these biological processes, which helps explain why cellulogia is significantly more common in women than in men.
Why Cellulogia Is So Common in Women
Cellulogia affects an estimated 80–90% of women at some point in their lives. This prevalence is largely due to hormonal differences, connective tissue structure, and fat distribution patterns.
Estrogen promotes fat storage in areas such as the thighs, hips, and buttocks—regions where cellulogia most commonly appears. It also influences vascular permeability, which can contribute to fluid accumulation in the interstitial space.
Additionally, women tend to have connective tissue septa arranged vertically, while men’s septa are more crisscrossed. This structural difference provides men with greater resistance to the upward pressure of fat cells, making cellulogia less visible.
Genetics also play a significant role. If close family members have noticeable cellulogia, the likelihood of developing it increases, regardless of lifestyle choices.
The Role of Genetics in Cellulogia
Genetics influence nearly every aspect of cellulogia, from fat cell size and distribution to connective tissue strength and skin elasticity. Some people are genetically predisposed to retain fluid more easily or have weaker collagen structures, both of which can contribute to the appearance of cellulogia.
Inherited differences in metabolism and hormone sensitivity also matter. For example, variations in estrogen receptors or enzymes involved in fat storage can make certain individuals more susceptible.
Skin thickness and elasticity, which are largely genetic traits, affect how visible cellulogia becomes. Thinner skin with reduced collagen content tends to reveal underlying irregularities more clearly.
Understanding the genetic component helps reframe cellulogia as a natural variation rather than something caused solely by lifestyle or personal choices.
Lifestyle Factors That Influence Cellulogia
While genetics and biology set the foundation, lifestyle factors can influence the severity and visibility of cellulogia. These factors do not “cause” cellulogia but can either support or challenge the body’s connective tissue and circulatory systems.
Sedentary behavior can reduce blood flow and lymphatic drainage, contributing to fluid retention. Prolonged sitting, especially with poor posture, may exacerbate these effects in the lower body.
Smoking negatively affects collagen production and microcirculation, potentially worsening skin texture. Chronic stress can also influence hormonal balance and inflammation, indirectly affecting cellulogia.
That said, even individuals with highly active lifestyles and balanced habits can experience cellulogia, reinforcing the idea that it is not a moral or health failing.
Nutrition and Its Relationship with Cellulogia
Nutrition plays a supportive role in overall skin and connective tissue health. Diets rich in whole foods, antioxidants, and adequate protein can help maintain collagen integrity and reduce inflammation.
Hydration is particularly important. Proper fluid intake supports lymphatic flow and helps prevent excessive fluid retention in tissues. Dehydration, paradoxically, can make cellulogia more noticeable.
Excessive intake of highly processed foods, refined sugars, and high sodium levels may contribute to inflammation and water retention. However, no single food causes or cures cellulogia.
A balanced approach to nutrition should be seen as a way to support general well-being rather than a targeted solution for eliminating skin texture variations.
Exercise and Movement: What Really Helps
Exercise improves circulation, supports muscle tone, and enhances lymphatic drainage—all factors that can influence the appearance of cellulogia. Strength training, in particular, can help by increasing muscle mass beneath the skin, creating a smoother overall contour.
Cardiovascular activities such as walking, cycling, and swimming promote blood flow and metabolic health. Consistent movement throughout the day is often more beneficial than occasional intense workouts.
However, it is crucial to manage expectations. Exercise may reduce the visibility of cellulogia but rarely eliminates it entirely. Even elite athletes commonly have some degree of skin dimpling.
Viewing exercise as a tool for health and strength rather than aesthetic perfection fosters a healthier relationship with the body.
The Psychological Impact of Cellulogia
The way cellulogia is portrayed in media has historically contributed to negative body image and unrealistic expectations. Many individuals experience unnecessary shame or anxiety over a completely normal physical trait.
Social media filters and edited images have further distorted perceptions, making natural skin textures appear abnormal. This can lead to a cycle of comparison and dissatisfaction.
A growing body of body-positive and body-neutral movements is helping shift the narrative. By acknowledging cellulogia as common and natural, these movements encourage acceptance and self-compassion.
Mental well-being is just as important as physical health, and reframing cellulogia can significantly reduce emotional distress.
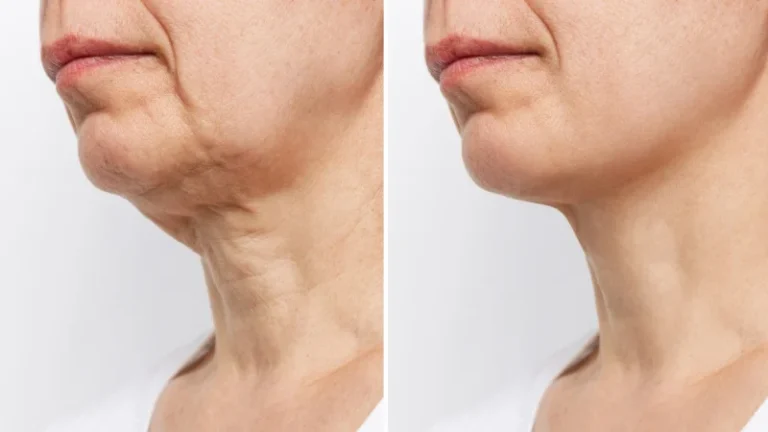
Cosmetic Treatments and Their Limitations
Numerous cosmetic treatments claim to reduce or eliminate cellulogia, ranging from topical creams to advanced medical procedures. While some methods can temporarily improve skin appearance, none offer permanent solutions.
Topical products may improve hydration and skin smoothness but cannot alter deep connective tissue structures. Massage-based techniques and devices can enhance circulation temporarily, leading to short-term visual improvements.
More invasive treatments, such as laser therapies or subcision, may offer longer-lasting results for some individuals. However, these procedures come with risks, costs, and varying effectiveness.
An informed, realistic approach is essential when considering any cosmetic intervention.
Cellulogia and Aging
Aging naturally affects skin elasticity, collagen production, and fat distribution, all of which can influence cellulogia. As collagen levels decline, the skin becomes thinner and less resilient, making underlying irregularities more visible.
Hormonal changes, particularly during menopause, can also affect fat storage and connective tissue health. Reduced estrogen levels may lead to changes in skin texture and firmness.
These changes are a normal part of the aging process and should be understood within the broader context of overall health and life experience.
Accepting these shifts can be empowering, especially when combined with self-care practices that prioritize comfort and vitality over appearance.
Cultural Perspectives on Cellulogia
Different cultures perceive cellulogia in different ways. In some societies, it is largely ignored or accepted as a natural part of the body, while in others it has been heavily commercialized as a problem to fix.
Western beauty standards have historically emphasized smooth, uniform skin, contributing to the widespread marketing of anti-cellulite products. However, global conversations around diversity and authenticity are gradually changing these norms.
As representation becomes more inclusive, natural skin textures are increasingly visible in advertising and media, helping normalize cellulogia across cultures.
Cultural awareness plays a key role in reshaping how we view and talk about the body.
Redefining Beauty and Body Acceptance
Cellulogia challenges narrow definitions of beauty that equate worth with flawlessness. By recognizing it as a common human trait, we open the door to more inclusive and realistic standards.
Body acceptance does not mean abandoning self-care or personal goals. Rather, it means pursuing health and well-being without tying self-esteem to physical perfection.
Education plays a powerful role in this shift. When people understand the science behind cellulogia, fear and misinformation lose their grip.
Ultimately, redefining beauty is about honoring the body for what it does, not just how it looks.
Final Thoughts on Cellulogia
Cellulogia is a natural, complex, and widely experienced phenomenon rooted in biology, genetics, and normal bodily function. It is not a condition that needs to be cured, hidden, or feared.